Processed Foods and Obesity

The rise in the U.S. calorie supply responsible for the obesity epidemic wasn’t just about more food, but a different kind of food.
The rise in the number of calories provided by the food supply since the 1970s “is more than sufficient to explain the US epidemic of obesity.” Similar spikes in calorie surplus were noted in developed countries around the world in parallel with and presumed to be primarily responsible for, the expanding waistlines of their populations. After taking exports into account, by the year 2000, the United States was producing 3,900 calories for every man, woman, and child—nearly twice as much as many people need.
It wasn’t always this way. The number of calories in the food supply actually declined over the first half of the twentieth century and only started its upward climb to unprecedented heights in the 1970s. The drop in the first half of the century was attributed to the reduction in hard manual labor. The population had decreased energy needs, so they ate decreased energy diets. They didn’t need all the extra calories. But then the “energy balance flipping point” occurred, when the “move less, stay lean phase” that existed throughout most of the century turned into the “eat more, gain weight phase” that plagues us to this day. So, what changed?
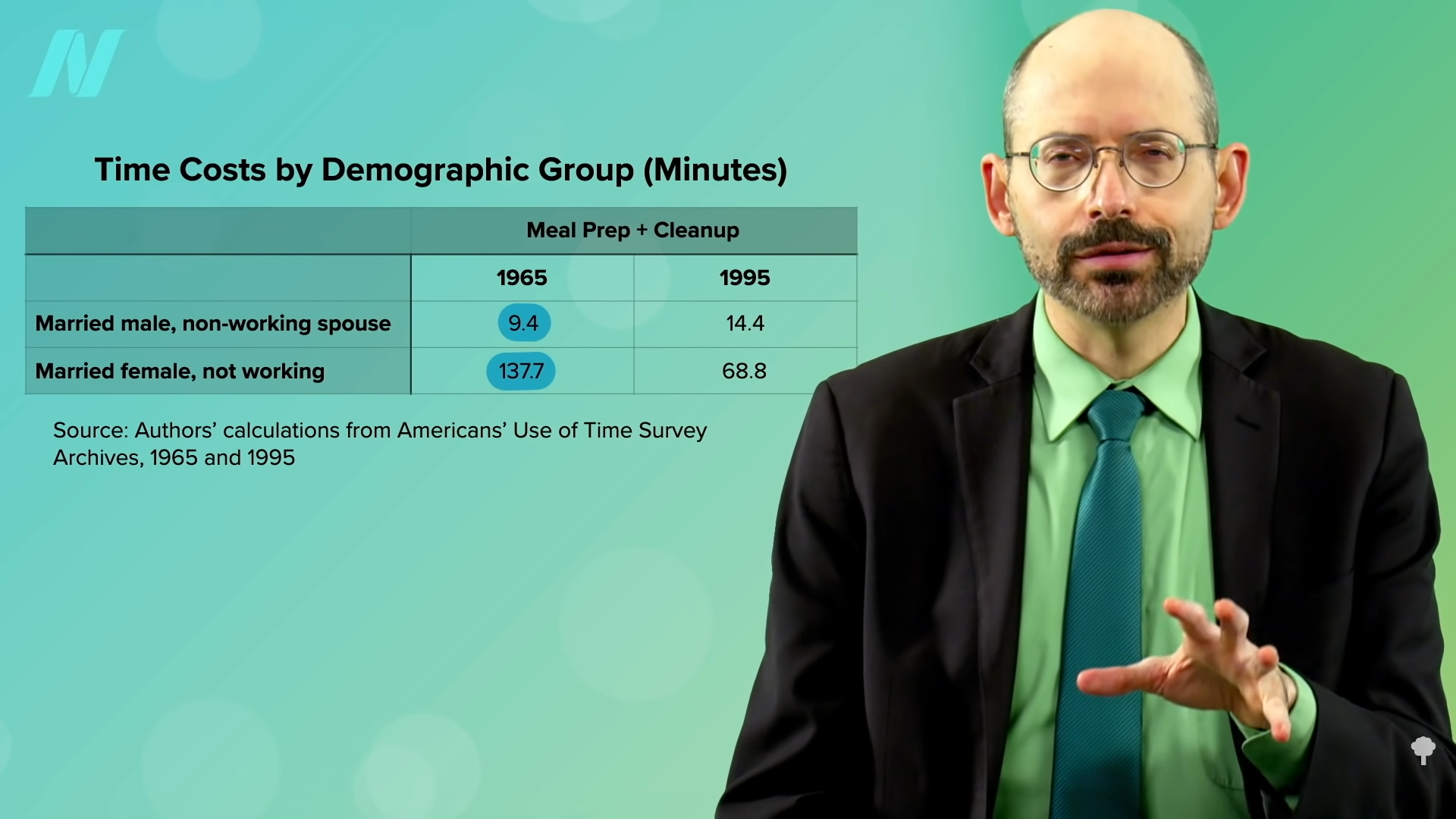
As I discuss in my video The Role of Processed Foods in the Obesity Epidemic, what happened in the 1970s was a revolution in the food industry. In the 1960s, most food was prepared and cooked in the home. The typical “married female, not working” spent hours a day cooking and cleaning up after meals. (The “married male, non-working spouse” averaged nine minutes, as you can see below and at 1:34 in my video.) But then a mixed-blessing transformation took place. Technological advances in food preservation and packaging enabled manufacturers to mass prepare and distribute food for ready consumption. The metamorphosis has been compared to what happened a century before with the mass production and supply of manufactured goods during the Industrial Revolution. But this time, they were just mass-producing food. Using new preservatives, artificial flavors, and techniques, such as deep freezing and vacuum packaging, food corporations could take advantage of economies of scale to mass produce “very durable, palatable, and ready-to-consume” edibles that offer “an enormous commercial advantage over fresh and perishable whole or minimally processed foods.”
Think ye of the Twinkie. With enough time and effort, “ambitious cooks” could create a cream-filled cake, but now they are available around every corner for less than a dollar. If every time someone wanted a Twinkie, they had to bake it themselves, they’d probably eat a lot fewer Twinkies. The packaged food sector is now a multitrillion-dollar industry.
Consider the humble potato. We’ve long been a nation of potato eaters, but we usually baked or boiled them. Anyone who’s made fries from scratch knows what a pain it is, with all the peeling, cutting, and splattering of oil. But with sophisticated machinations of mechanization, production became centralized and fries could be shipped at -40°F to any fast-food deep-fat fryer or frozen food section in the country to become “America’s favorite vegetable.” Nearly all the increase in potato consumption in recent decades has been in the form of french fries and potato chips.
Cigarette production offers a compelling parallel. Up until automated rolling machines were invented, cigarettes had to be rolled by hand. It took 50 workers to produce the same number of cigarettes a machine could make in a minute. The price plunged and production leapt into the billions. Cigarette smoking went from being “relatively uncommon” to being almost everywhere. In the 20th century, the average per capita cigarette consumption rose from 54 cigarettes a year to 4,345 cigarettes “just before the first landmark Surgeon General’s Report” in 1964. The average American went from smoking about one cigarette a week to half a pack a day.
Tobacco itself was just as addictive before and after mass marketing. What changed was cheap, easy access. French fries have always been tasty, but they went from being rare, even in restaurants, to being accessible around each and every corner (likely next to the gas station where you can get your Twinkies and cigarettes).
The first Twinkie dates back to 1930, though, and Ore-Ida started selling frozen french fries in the 1950s. There has to be more to the story than just technological innovation, and we’ll explore that next.
This explosion of processed junk was aided and abetted by Big Government at the behest of Big Food, which I explore in my video The Role of Taxpayer Subsidies in the Obesity Epidemic.
This is the fifth video in an 11-part series. Here are the first four:
Videos still to come are listed in the related videos below.

